# Data augmentation
{:.no_toc}
## The goal
What is available as data augmentation methods in torchvision?
Questions to [David Rotermund](mailto:davrot@uni-bremen.de)
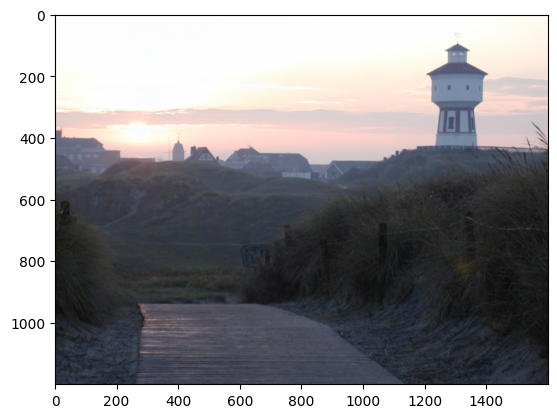
Initial Image:
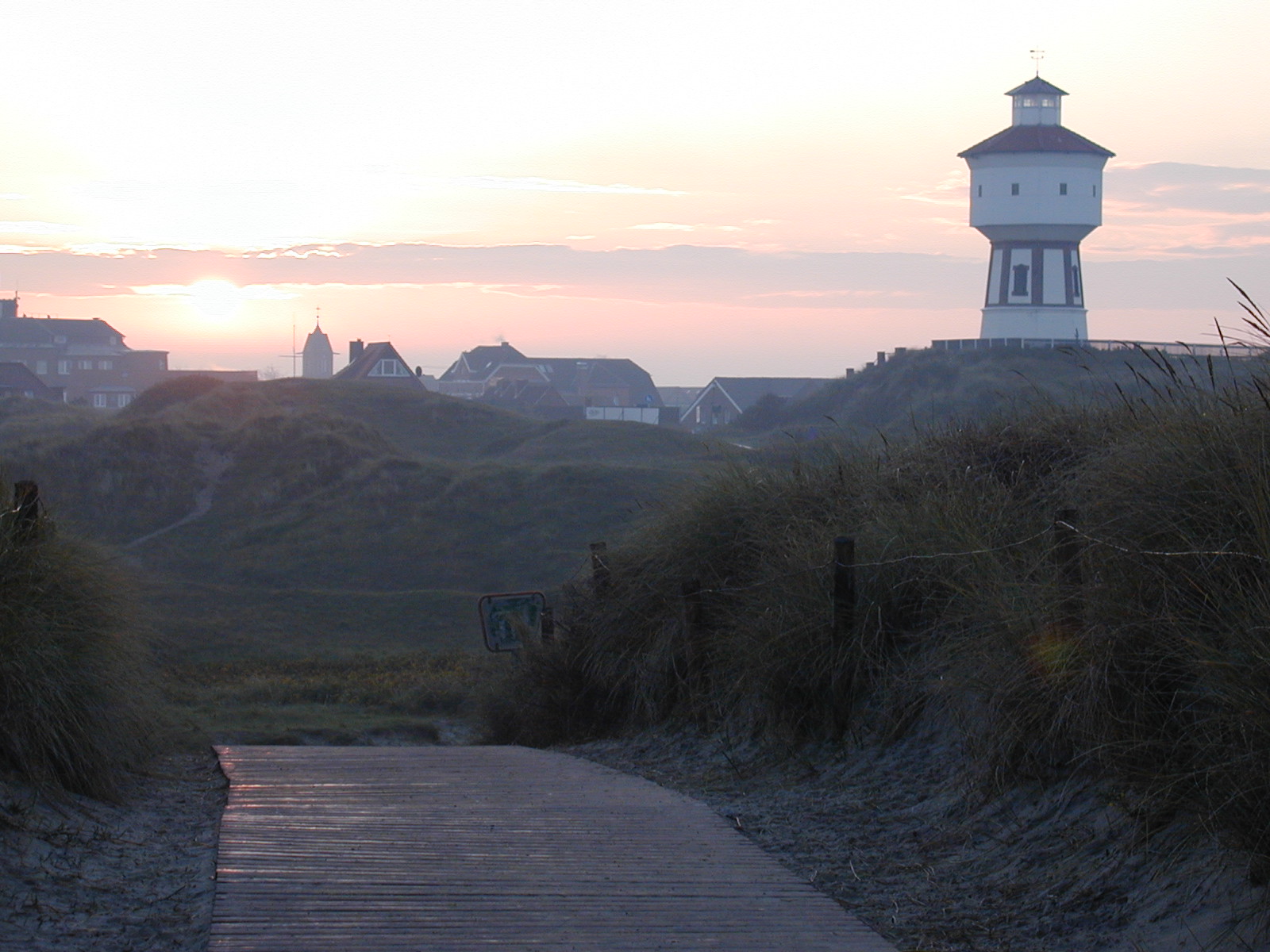

Photo by Udo Ernst
## Loading an example image (with opencv2)
Load it via [cv2.imread( filename[, flags]) -> retval](https://docs.opencv.org/4.5.3/d4/da8/group__imgcodecs.html#ga288b8b3da0892bd651fce07b3bbd3a56)
```python
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
filename: str = "data_augmentation_test_image.jpg"
original_image = cv2.imread(filename)
plt.imshow(original_image)
plt.show()
```
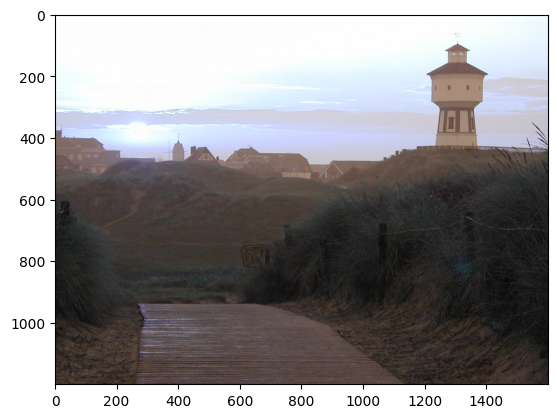
As you can see (not very well I might add) is that the color channels are wrong. But may be we want no color anyway ( options can be found [here](https://docs.opencv.org/4.5.3/d8/d6a/group__imgcodecs__flags.html#ga61d9b0126a3e57d9277ac48327799c80) ):
```python
original_image = cv2.imread(filename, cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
plt.imshow(original_image, cmap="gray")
plt.show()
```

```python
import numpy as np
original_image = cv2.imread(filename, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
# "Convert" from BlueGreenRed (BGR) to RGB (RedGreenBlue)
# This is a flip in the third dimension.
original_image = np.flip(original_image, axis=2)
plt.imshow(original_image)
plt.show()
```
## Torchvision: A selection of transformations
### Into PyTorch
First we need to convert the np.ndarray into a suitable torch tensor

```python
import torch
torch_image = torch.tensor(
np.moveaxis(original_image.astype(dtype=np.float32) / 255.0, 2, 0)
)
print(torch_image.shape) # -> torch.Size([3, 1200, 1600])
```
Note: For the following random opertions, we can control the random seed of torch via [torch.manual_seed(seed)](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.manual_seed.html).
Some example transformations from [torchvision](https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/transforms.html):
### [torchvision.transforms.Pad(padding, fill=0, padding_mode='constant') ](https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/transforms.html#torchvision.transforms.Pad)
```python
import torchvision as tv
pad_transform = tv.transforms.Pad(padding=(50, 100), fill=0.5)
new_image = pad_transform(torch_image)
plt.imshow(np.moveaxis(new_image.detach().numpy(), 0, 2))
plt.show()
```

### [torchvision.transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(p=0.5)](https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/transforms.html#torchvision.transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip)
Horizontally flip the given image randomly with a given probability.
### [torchvision.transforms.RandomVerticalFlip(p=0.5)](https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/transforms.html#torchvision.transforms.RandomVerticalFlip)
Vertically flip the given image randomly with a given probability.
### [torchvision.transforms.Resize(size, interpolation=, max_size=None, antialias=None)](https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/transforms.html#torchvision.transforms.Pad)
The Resize transform resizes an image.
```python
resize_transform = tv.transforms.Resize(size=(50, 100))
new_image = resize_transform(torch_image)
plt.imshow(np.moveaxis(new_image.detach().numpy(), 0, 2))
plt.show()
```

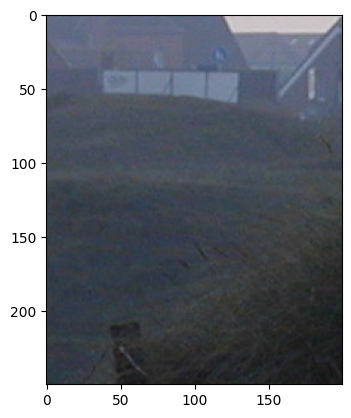
### [torchvision.transforms.CenterCrop(size)](https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/transforms.html#torchvision.transforms.CenterCrop)
The CenterCrop transform crops the given image at the center.
```python
center_crop_transform = tv.transforms.CenterCrop(size=(250, 200))
new_image = center_crop_transform(torch_image)
plt.imshow(np.moveaxis(new_image.detach().numpy(), 0, 2))
plt.show()
```
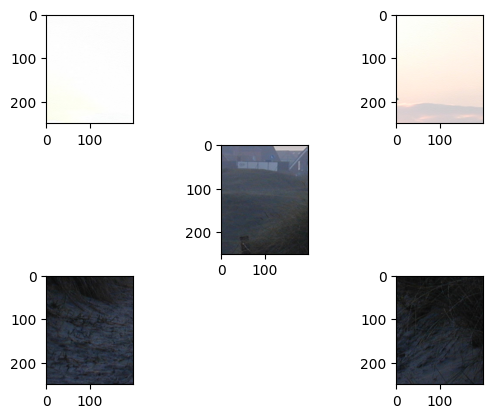
### [torchvision.transforms.FiveCrop(size)](https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/transforms.html#torchvision.transforms.FiveCrop)
The FiveCrop transform crops the given image into four corners and the central crop.
```python
position = (1, 3, 7, 9, 5)
five_crop_transform = tv.transforms.FiveCrop(size=(250, 200))
new_image = five_crop_transform(torch_image)
for i, p in enumerate(position):
plt.subplot(3, 3, p)
plt.imshow(np.moveaxis(new_image[i].detach().numpy(), 0, 2))
plt.show()
```
### [torchvision.transforms.TenCrop(size, vertical_flip=False)](https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/transforms.html#torchvision.transforms.Scale)
Crop the given image into four corners and the central crop plus the flipped version of these (horizontal flipping is used by default).
### [torchvision.transforms.Grayscale(num_output_channels=1)](https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/transforms.html#torchvision.transforms.Grayscale)
The Grayscale transform converts an image to grayscale.
```python
gray_transform = tv.transforms.Grayscale()
new_image = gray_transform(torch_image)
plt.imshow(new_image.squeeze().detach().numpy(), cmap="gray")
plt.show()
```

### [torchvision.transforms.RandomGrayscale(p=0.1)](https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/transforms.html#torchvision.transforms.RandomGrayscale)
Randomly convert image to grayscale with a probability of p (default 0.1).
### [torchvision.transforms.RandomInvert(p=0.5)](https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/transforms.html#torchvision.transforms.RandomInvert)
Inverts the colors of the given image randomly with a given probability.
```python
random_invert_transform = tv.transforms.RandomInvert(p=0.5)
for i in range(1, 3):
new_image = random_invert_transform(torch_image)
plt.subplot(2, 1, i)
plt.imshow(np.moveaxis(new_image.detach().numpy(), 0, 2))
plt.show()
```
### [torchvision.transforms.Normalize(mean, std, inplace=False)](https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/transforms.html#torchvision.transforms.Normalize)
Normalize a tensor image with mean and standard deviation.
### [torchvision.transforms.RandomEqualize(p=0.5)](https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/transforms.html#torchvision.transforms.RandomEqualize)
Equalize the histogram of the given image randomly with a given probability.
### [torchvision.transforms.ColorJitter(brightness=0, contrast=0, saturation=0, hue=0)](https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/transforms.html#torchvision.transforms.ColorJitter)
The ColorJitter transform randomly changes the brightness, saturation, and other properties of an image.
```python
color_jitter_transform = tv.transforms.ColorJitter(brightness=0.75, hue=0.5)
for i in range(1, 10):
new_image = color_jitter_transform(torch_image)
plt.subplot(3, 3, i)
plt.imshow(np.moveaxis(new_image.detach().numpy(), 0, 2))
plt.show()
```

### [torchvision.transforms.GaussianBlur(kernel_size, sigma=(0.1, 2.0))](https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/transforms.html#torchvision.transforms.GaussianBlur)
The GaussianBlur transform performs gaussian blur transform on an image.
Note: Big kernel sizes are slow. (51,51) is rather big. Kernel size needs to be odd and positive.
```python
gauss_transform = tv.transforms.GaussianBlur(kernel_size=(101, 101), sigma=(0.1, 10))
new_image = gauss_transform(torch_image)
plt.imshow(np.moveaxis(new_image.detach().numpy(), 0, 2))
plt.show()
```
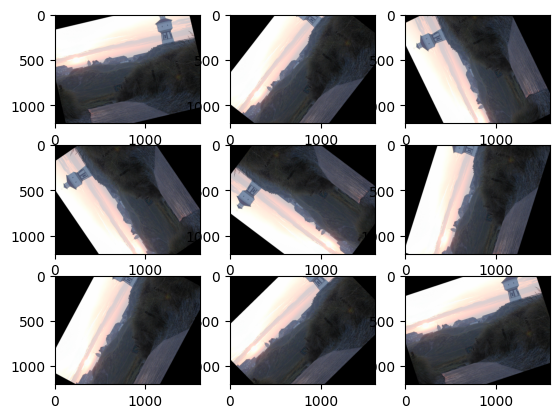
### [torchvision.transforms.RandomPerspective(distortion_scale=0.5, p=0.5, interpolation=, fill=0)](https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/transforms.html#torchvision.transforms.RandomPerspective)
The RandomPerspective transform performs random perspective transform on an image.
```python
random_perspective_transform = tv.transforms.RandomPerspective(
distortion_scale=0.6, p=1.0
)
for i in range(1, 10):
new_image = random_perspective_transform(torch_image)
plt.subplot(3, 3, i)
plt.imshow(np.moveaxis(new_image.detach().numpy(), 0, 2))
plt.show()
```

### [torchvision.transforms.RandomRotation(degrees, interpolation=, expand=False, center=None, fill=0, resample=None)](https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/transforms.html#torchvision.transforms.RandomRotation)
The RandomRotation transform rotates an image with random angle.
```python
random_rotation_transform = tv.transforms.RandomRotation(degrees=(0, 180))
for i in range(1, 10):
new_image = random_rotation_transform(torch_image)
plt.subplot(3, 3, i)
plt.imshow(np.moveaxis(new_image.detach().numpy(), 0, 2))
plt.show()
```
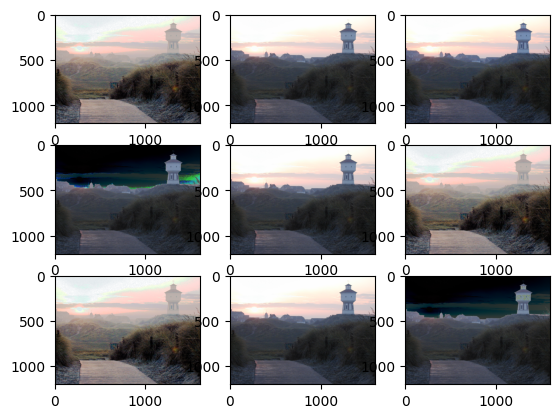
### [torchvision.transforms.RandomAffine(degrees, translate=None, scale=None, shear=None, interpolation=, fill=0, fillcolor=None, resample=None)](https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/transforms.html#torchvision.transforms.RandomAffine)
The RandomAffine transform performs random affine transform on an image.
```python
random_affine_transform = tv.transforms.RandomAffine(degrees=(0, 180))
for i in range(1, 10):
new_image = random_affine_transform(torch_image)
plt.subplot(3, 3, i)
plt.imshow(np.moveaxis(new_image.detach().numpy(), 0, 2))
plt.show()
```

### [torchvision.transforms.RandomCrop(size, padding=None, pad_if_needed=False, fill=0, padding_mode='constant')](https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/transforms.html#torchvision.transforms.RandomCrop)
The RandomCrop transform crops an image at a random location.
```python
random_crop_transform = tv.transforms.RandomCrop(size=(250, 200))
for i in range(1, 10):
new_image = random_crop_transform(torch_image)
plt.subplot(3, 3, i)
plt.imshow(np.moveaxis(new_image.detach().numpy(), 0, 2))
plt.show()
```

### [torchvision.transforms.RandomResizedCrop(size, scale=(0.08, 1.0), ratio=(0.75, 1.3333333333333333), interpolation=)](https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/transforms.html#torchvision.transforms.RandomResizedCrop)
The RandomResizedCrop transform crops an image at a random location, and then resizes the crop to a given size.
### [torchvision.transforms.RandomPosterize(bits, p=0.5)](https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/transforms.html#torchvision.transforms.RandomPosterize)
Posterize the image randomly with a given probability by reducing the number of bits for each color channel.
```python
for i in range(1, 5):
random_posterize_transform = tv.transforms.RandomPosterize(bits=i, p=1.0)
new_image = random_posterize_transform((torch_image * 255).type(dtype=torch.uint8))
plt.subplot(2, 2, i)
plt.imshow(np.moveaxis(new_image.detach().numpy(), 0, 2))
plt.show()
```

### [torchvision.transforms.RandomSolarize(threshold, p=0.5)](https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/transforms.html#torchvision.transforms.RandomSolarize)
Solarize the image randomly with a given probability by inverting all pixel values above a threshold.
```python
random_solarize_transform = tv.transforms.RandomSolarize(threshold=0.5)
new_image = random_solarize_transform(torch_image)
plt.imshow(np.moveaxis(new_image.detach().numpy(), 0, 2))
plt.show()
```

### [torchvision.transforms.RandomAdjustSharpness(sharpness_factor, p=0.5)](https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/transforms.html#torchvision.transforms.RandomAdjustSharpness)
Adjust the sharpness of the image randomly with a given probability.
```python
random_sharpness_transform = tv.transforms.RandomAdjustSharpness(
sharpness_factor=50, p=1.0
)
new_image = random_sharpness_transform(torch_image)
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.imshow(np.moveaxis(torch_image.detach().numpy(), 0, 2))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.imshow(np.moveaxis(new_image.detach().numpy(), 0, 2))
plt.show()
```

### [torchvision.transforms.RandomAutocontrast(p=0.5)](https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/transforms.html#torchvision.transforms.RandomAutocontrast)
Autocontrast the pixels of the given image randomly with a given probability.
I don't see any effect.
```python
random_autocontrast_transform = tv.transforms.RandomAutocontrast(p=1.0)
new_image = random_autocontrast_transform(torch_image)
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.imshow(np.moveaxis(torch_image.detach().numpy(), 0, 2))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.imshow(np.moveaxis(new_image.detach().numpy(), 0, 2))
plt.show()
```

### [torchvision.transforms.RandomErasing(p=0.5, scale=(0.02, 0.33), ratio=(0.3, 3.3), value=0, inplace=False)](https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/transforms.html#torchvision.transforms.RandomErasing)
Randomly selects a rectangle region in an torch Tensor image and erases its pixels.
```python
random_erasing_transform = tv.transforms.RandomErasing(p=1.0)
new_image = random_erasing_transform(torch_image)
plt.imshow(np.moveaxis(new_image.detach().numpy(), 0, 2))
plt.show()
```

## Predefined processing chains
[torchvision.transforms.AutoAugment(policy: torchvision.transforms.autoaugment.AutoAugmentPolicy = , interpolation: torchvision.transforms.functional.InterpolationMode = , fill: Optional[List[float]] = None)](https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/transforms.html#torchvision.transforms.AutoAugment)
AutoAugment data augmentation method based on [“AutoAugment: Learning Augmentation Strategies from Data”](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1805.09501.pdf).
[torchvision.transforms.AutoAugmentPolicy(value)](https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/transforms.html#torchvision.transforms.AutoAugmentPolicy)
AutoAugment policies learned on different datasets. Available policies are IMAGENET, CIFAR10 and SVHN.
#### CIFAR10
```python
random_auto1_transform = tv.transforms.AutoAugment(
tv.transforms.AutoAugmentPolicy.CIFAR10
)
for i in range(1, 10):
new_image = random_auto1_transform((torch_image * 255).type(dtype=torch.uint8))
plt.subplot(3, 3, i)
plt.imshow(np.moveaxis(new_image.detach().numpy(), 0, 2))
plt.show()
```
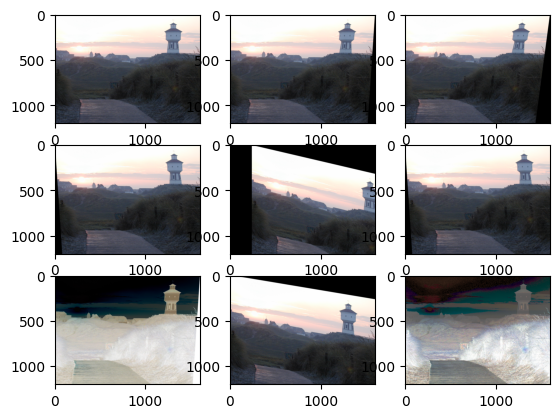
#### IMAGENET
```python
random_auto2_transform = tv.transforms.AutoAugment(
tv.transforms.AutoAugmentPolicy.IMAGENET
)
for i in range(1, 10):
new_image = random_auto2_transform((torch_image * 255).type(dtype=torch.uint8))
plt.subplot(3, 3, i)
plt.imshow(np.moveaxis(new_image.detach().numpy(), 0, 2))
plt.show()
```

#### SVHN
```python
random_auto3_transform = tv.transforms.AutoAugment(tv.transforms.AutoAugmentPolicy.SVHN)
for i in range(1, 10):
new_image = random_auto3_transform((torch_image * 255).type(dtype=torch.uint8))
plt.subplot(3, 3, i)
plt.imshow(np.moveaxis(new_image.detach().numpy(), 0, 2))
plt.show()
```
## Building custom processing chains
### [torch.nn.Sequential(*args)](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.Sequential.html#torch.nn.Sequential)
A sequential container. Modules will be added to it in the order they are passed in the constructor.
```python
sequential_transform = torch.nn.Sequential(
tv.transforms.RandomSolarize(threshold=0.5, p=1.0),
tv.transforms.RandomErasing(p=1.0),
)
new_image = sequential_transform((torch_image * 255).type(dtype=torch.uint8))
plt.imshow(np.moveaxis(new_image.detach().numpy(), 0, 2))
plt.show()
```
Depending on the transformation used, I can be possible to just-in-time (jit) compile it.
```python
sequential_transform_jit = torch.jit.script(sequential_transform)
```

### [torchvision.transforms.Compose(transforms)](https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/transforms.html#torchvision.transforms.Compose)
Composes several transforms together. **This transform does not support torchscript.**
```python
compose_transform = tv.transforms.Compose(
[
tv.transforms.RandomSolarize(threshold=0.5, p=1.0),
tv.transforms.RandomErasing(p=1.0),
]
)
new_image = compose_transform((torch_image * 255).type(dtype=torch.uint8))
plt.imshow(np.moveaxis(new_image.detach().numpy(), 0, 2))
plt.show()
```

### [torchvision.transforms.RandomApply(transforms, p=0.5)](https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/transforms.html#torchvision.transforms.RandomApply)
Apply randomly a list of transformations with a given probability.
**Note: It randomly applies the whole list of transformation or none.**
```python
randomapply_transform = tv.transforms.RandomApply(
[
tv.transforms.RandomSolarize(threshold=0.5, p=1.0),
tv.transforms.RandomErasing(p=1.0),
],
p=0.5,
)
for i in range(1, 3):
plt.subplot(2, 1, i)
new_image = randomapply_transform((torch_image * 255).type(dtype=torch.uint8))
plt.imshow(np.moveaxis(new_image.detach().numpy(), 0, 2))
plt.show()
```
## Building your own filter
In the case you need a special filter then you just can write it very easily on your own. Here is an example.
```python
import torch
class OnOffFilter(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, p: float = 0.5) -> None:
super(OnOffFilter, self).__init__()
self.p: float = p
def forward(self, tensor: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
assert tensor.shape[1] == 1
tensor -= self.p
temp_0: torch.Tensor = torch.where(
tensor < 0.0, -tensor, tensor.new_zeros(tensor.shape, dtype=tensor.dtype)
)
temp_1: torch.Tensor = torch.where(
tensor >= 0.0, tensor, tensor.new_zeros(tensor.shape, dtype=tensor.dtype)
)
new_tensor: torch.Tensor = torch.cat((temp_0, temp_1), dim=1)
return new_tensor
def __repr__(self):
return self.__class__.__name__ + "(p={0})".format(self.p)
if __name__ == "__main__":
pass
```