mirror of
https://github.com/davrot/pytutorial.git
synced 2025-07-04 05:00:02 +02:00
|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| image1.png | ||
| image2.png | ||
| image3.png | ||
| README.md | ||
Remove a common signal from your data
Goal
We want to remove a common signal which was mixed on top a set of data channels. There are many methods to do so. We will use SVD. Implementations are for example: scipy.linalg.svd or torch.svd_lowrank (which also works on the GPU)
Questions to David Rotermund
Creating dirty test data
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
rng = np.random.default_rng()
time_series_length: int = 1000
number_of_channels: int = 3
# Clean data
clean_data: np.ndarray = (
rng.random((time_series_length, number_of_channels))
+ 5 * np.arange(0, number_of_channels)[np.newaxis, ...]
)
# Perturbation
t: np.ndarray = np.arange(0, time_series_length) / 1000
y: np.ndarray = np.sin(t * 2 * np.pi * 1)
mix_coefficients: np.ndarray = 1 + rng.random((3))
perturbation: np.ndarray = y[..., np.newaxis] * mix_coefficients[np.newaxis, ...]
# Dirty data
dirty_data: np.ndarray = clean_data.copy()
dirty_data += perturbation
np.savez(
"data.npz", clean_data=clean_data, perturbation=perturbation, dirty_data=dirty_data
)
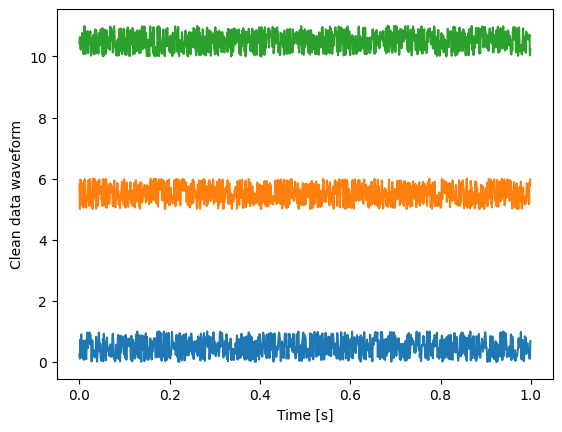
plt.plot(t, clean_data)
plt.xlabel("Time [s]")
plt.ylabel("Clean data waveform")
plt.show()
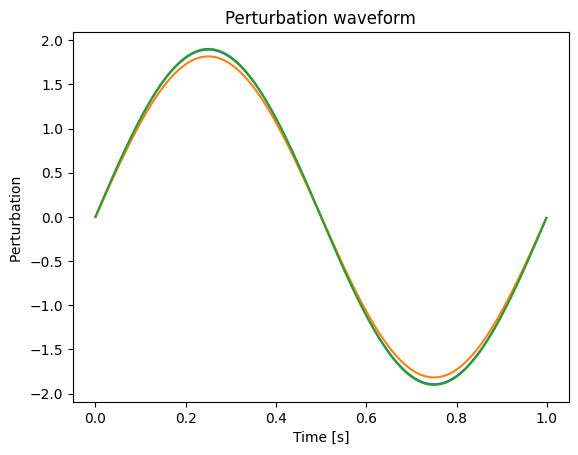
plt.plot(t, perturbation)
plt.xlabel("Time [s]")
plt.ylabel("Perturbation ")
plt.title("Perturbation waveform")
plt.show()
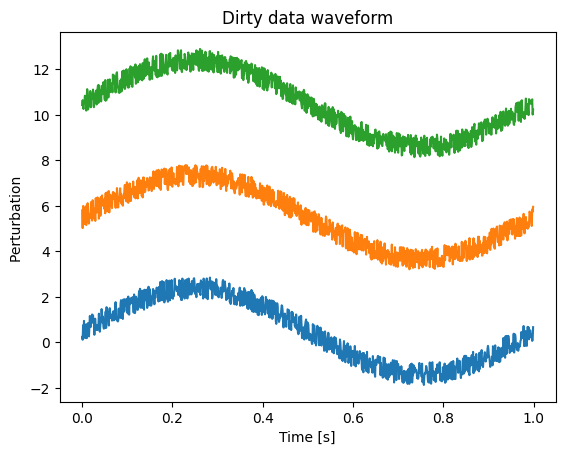
plt.plot(t, dirty_data)
plt.xlabel("Time [s]")
plt.ylabel("Dirty data waveform ")
plt.title("Dirty data waveform")
plt.show()
We get three fully random time series
Sine wave with random amplitudes as common perturbation
Both combined with random mixing coefficients