mirror of
https://github.com/davrot/pytutorial.git
synced 2025-07-11 07:00:04 +02:00
|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| image1.png | ||
| image2.png | ||
| image3.png | ||
| README.md | ||
ROC
{:.no_toc}
* TOC {:toc}Top
Questions to David Rotermund
The following code is for the case where the amount of data for both classes is the same.
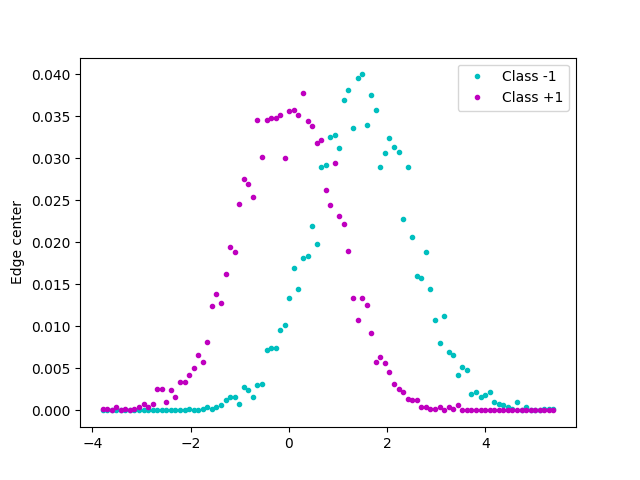
Test data
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
rng = np.random.default_rng(1)
a_x = rng.normal(1.5, 1.0, size=(5000))
b_x = rng.normal(0.0, 1.0, size=(5000))
ab_x = np.concatenate([a_x, b_x])
edges = np.histogram_bin_edges(ab_x, bins=100, range=None, weights=None)
h_a, _ = np.histogram(a_x, bins=edges)
h_b, _ = np.histogram(b_x, bins=edges)
h_a = h_a.astype(np.float32)
h_b = h_b.astype(np.float32)
h_a /= h_a.sum()
h_b /= h_b.sum()
edges = (edges[1:] + edges[:-1]) / 2.0
plt.plot(edges, h_a, "c.", label="Class -1")
plt.plot(edges, h_b, "m.", label="Class +1")
plt.ylabel("Probability of a value")
plt.ylabel("Edge center")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
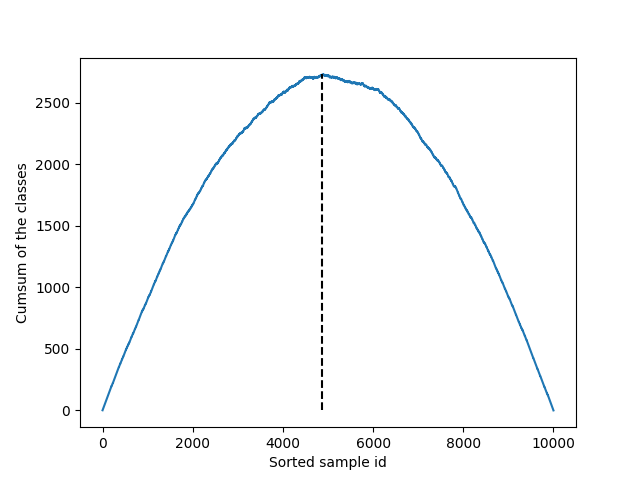
Find the cumsum maximum
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
rng = np.random.default_rng(1)
a_x = rng.normal(1.5, 1.0, size=(5000))
b_x = rng.normal(0.0, 1.0, size=(5000))
data_data = np.concatenate([a_x, b_x])
data_class = np.concatenate([np.full_like(a_x, -1), np.full_like(b_x, +1)])
idx = np.argsort(data_data)
data_data = data_data[idx]
data_class = data_class[idx]
data_cumsum = np.cumsum(data_class)
plt.plot(data_cumsum)
plt.plot(
[np.argmax(data_cumsum), np.argmax(data_cumsum)], [0, np.max(data_cumsum)], "k--"
)
plt.ylabel("Cumsum of the classes")
plt.xlabel("Sorted sample id")
plt.show()
How to create an estimate from the ROC cumsum maximum
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
rng = np.random.default_rng(1)
a_x = rng.normal(1.5, 1.0, size=(5000))
b_x = rng.normal(0.0, 1.0, size=(5000))
data_data = np.concatenate([a_x, b_x])
data_class = np.concatenate([np.full_like(a_x, -1), np.full_like(b_x, +1)])
idx = np.argsort(data_data)
data_data = data_data[idx]
data_class = data_class[idx]
data_cumsum = np.cumsum(data_class)
border = np.argmax(np.abs(data_cumsum))
variant_a = (data_class[:border] == -1).sum() + (data_class[border:] == +1).sum()
variant_b = (data_class[:border] == +1).sum() + (data_class[border:] == -1).sum()
estimate_a = np.concatenate(
(np.full_like(data_class[:border], -1), np.full_like(data_class[border:], +1))
)
estimate_b = np.concatenate(
(np.full_like(data_class[:border], +1), np.full_like(data_class[border:], -1))
)
if variant_a > variant_b:
print("We will use: Estimate A")
estimate = estimate_a
else:
print("We will use: Estimate B")
estimate = estimate_b
performance = 100.0 * (data_class == estimate).sum() / data_class.shape[0]
print(f"Performance: {performance}% correct")
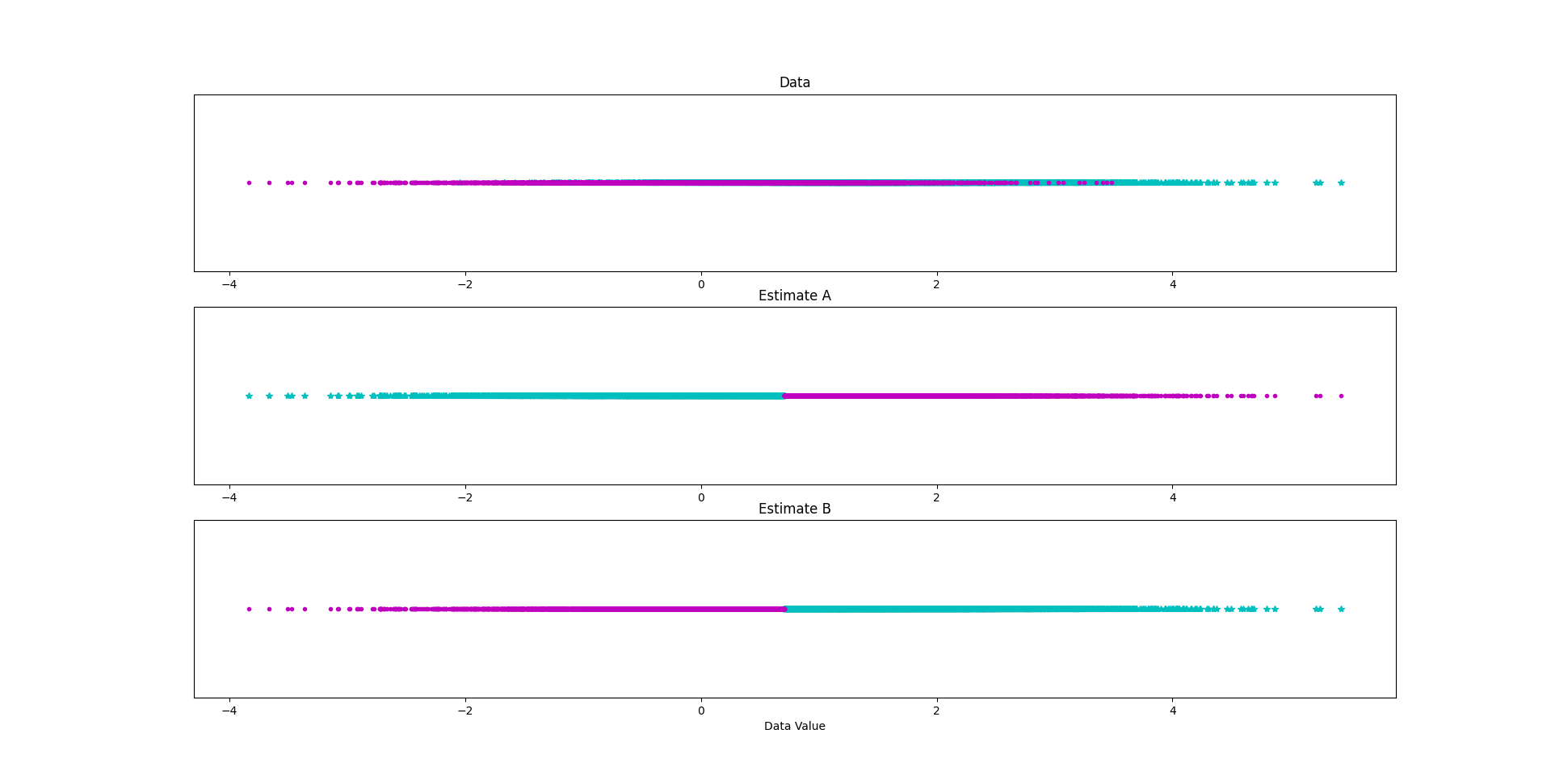
plt.subplot(3, 1, 1)
idx_a = np.where(data_class == -1)[0]
idx_b = np.where(data_class == +1)[0]
idx = np.arange(0, data_class.shape[0])
plt.plot(data_data[idx_a], np.zeros_like(idx_a), "c*")
plt.plot(data_data[idx_b], np.zeros_like(idx_b), "m.")
plt.yticks([])
plt.title("Data")
plt.subplot(3, 1, 2)
idx_a = np.where(estimate_a == -1)[0]
idx_b = np.where(estimate_a == +1)[0]
idx = np.arange(0, estimate_a.shape[0])
plt.plot(data_data[idx_a], np.zeros_like(idx_a), "c*")
plt.plot(data_data[idx_b], np.zeros_like(idx_b), "m.")
plt.yticks([])
plt.title("Estimate A")
plt.subplot(3, 1, 3)
idx_a = np.where(estimate_b == -1)[0]
idx_b = np.where(estimate_b == +1)[0]
idx = np.arange(0, estimate_b.shape[0])
plt.plot(data_data[idx_a], np.zeros_like(idx_a), "c*")
plt.plot(data_data[idx_b], np.zeros_like(idx_b), "m.")
plt.yticks([])
plt.title("Estimate B")
plt.xlabel("Data Value")
plt.show()
Output:
We will use: Estimate B
Performance: 77.3% correct