mirror of
https://github.com/davrot/pytutorial.git
synced 2025-07-14 15:00:02 +02:00
|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| image1.png | ||
| image2.png | ||
| image3.png | ||
| README.md | ||
ROC
{:.no_toc}
* TOC {:toc}Top
Questions to David Rotermund
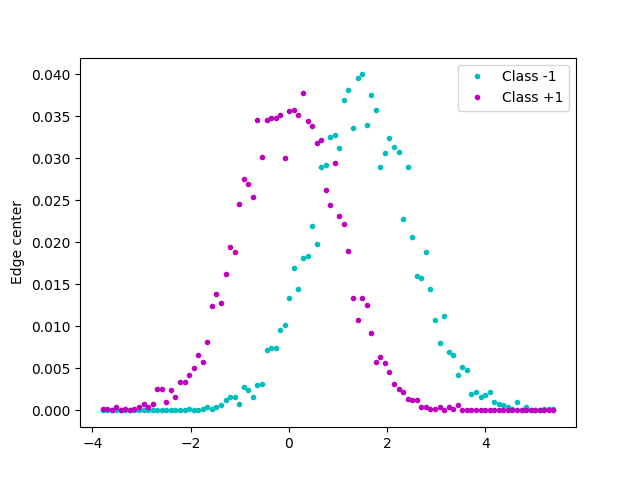
Test data
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
rng = np.random.default_rng(1)
a_x = rng.normal(1.5, 1.0, size=(5000))
b_x = rng.normal(0.0, 1.0, size=(5000))
ab_x = np.concatenate([a_x, b_x])
edges = np.histogram_bin_edges(ab_x, bins=100, range=None, weights=None)
h_a, _ = np.histogram(a_x, bins=edges)
h_b, _ = np.histogram(b_x, bins=edges)
h_a = h_a.astype(np.float32)
h_b = h_b.astype(np.float32)
h_a /= h_a.sum()
h_b /= h_b.sum()
edges = (edges[1:] + edges[:-1]) / 2.0
plt.plot(edges, h_a, "c.", label="Class -1")
plt.plot(edges, h_b, "m.", label="Class +1")
plt.ylabel("Probability of a value")
plt.ylabel("Edge center")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
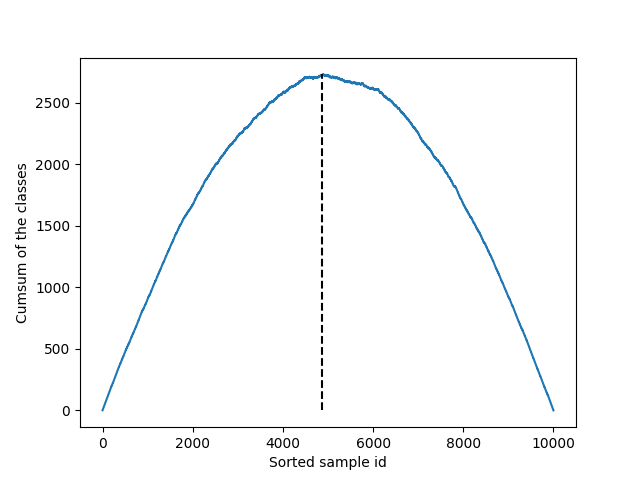
Find the cumsum maximum
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
rng = np.random.default_rng(1)
a_x = rng.normal(1.5, 1.0, size=(5000))
b_x = rng.normal(0.0, 1.0, size=(5000))
data_data = np.concatenate([a_x, b_x])
data_class = np.concatenate([np.full_like(a_x, -1), np.full_like(b_x, +1)])
idx = np.argsort(data_data)
data_data = data_data[idx]
data_class = data_class[idx]
data_cumsum = np.cumsum(data_class)
plt.plot(data_cumsum)
plt.plot(
[np.argmax(data_cumsum), np.argmax(data_cumsum)], [0, np.max(data_cumsum)], "k--"
)
plt.ylabel("Cumsum of the classes")
plt.xlabel("Sorted sample id")
plt.show()
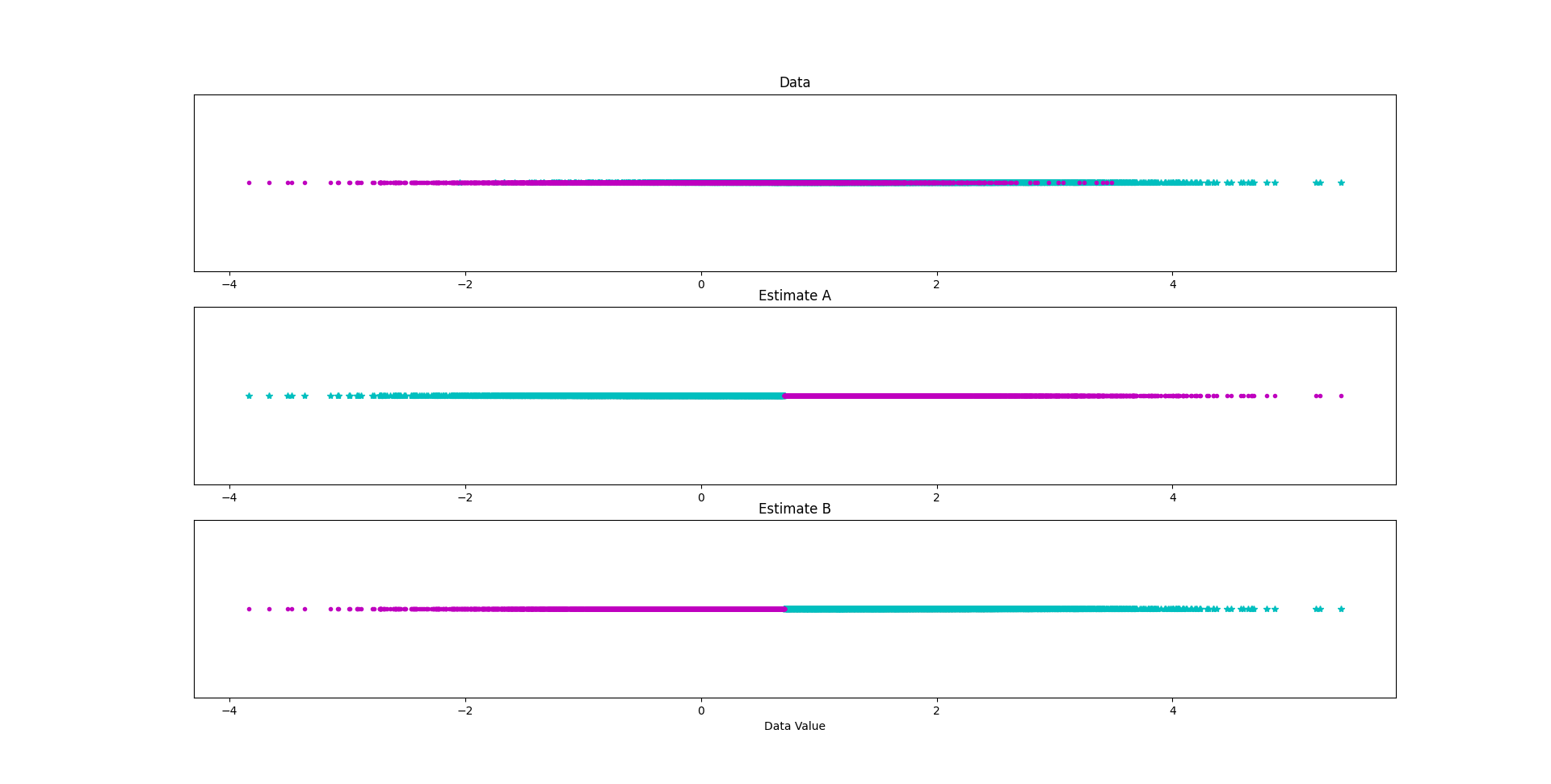
How to create an estimate from the ROC cumsum maximum
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
rng = np.random.default_rng(1)
a_x = rng.normal(1.5, 1.0, size=(5000))
b_x = rng.normal(0.0, 1.0, size=(5000))
data_data = np.concatenate([a_x, b_x])
data_class = np.concatenate([np.full_like(a_x, -1), np.full_like(b_x, +1)])
idx = np.argsort(data_data)
data_data = data_data[idx]
data_class = data_class[idx]
data_cumsum = np.cumsum(data_class)
border = np.argmax(data_cumsum)
variant_a = (data_class[:border] == -1).sum() + (data_class[border:] == +1).sum()
variant_b = (data_class[:border] == +1).sum() + (data_class[border:] == -1).sum()
estimate_a = np.concatenate(
(np.full_like(data_class[:border], -1), np.full_like(data_class[border:], +1))
)
estimate_b = np.concatenate(
(np.full_like(data_class[:border], +1), np.full_like(data_class[border:], -1))
)
if variant_a > variant_b:
print("We will use: Estimate A")
estimate = estimate_a
else:
print("We will use: Estimate B")
estimate = estimate_b
performance = 100.0 * (data_class == estimate).sum() / data_class.shape[0]
print(f"Performance: {performance}% correct")
plt.subplot(3, 1, 1)
idx_a = np.where(data_class == -1)[0]
idx_b = np.where(data_class == +1)[0]
idx = np.arange(0, data_class.shape[0])
plt.plot(data_data[idx_a], np.zeros_like(idx_a), "c*")
plt.plot(data_data[idx_b], np.zeros_like(idx_b), "m.")
plt.yticks([])
plt.title("Data")
plt.subplot(3, 1, 2)
idx_a = np.where(estimate_a == -1)[0]
idx_b = np.where(estimate_a == +1)[0]
idx = np.arange(0, estimate_a.shape[0])
plt.plot(data_data[idx_a], np.zeros_like(idx_a), "c*")
plt.plot(data_data[idx_b], np.zeros_like(idx_b), "m.")
plt.yticks([])
plt.title("Estimate A")
plt.subplot(3, 1, 3)
idx_a = np.where(estimate_b == -1)[0]
idx_b = np.where(estimate_b == +1)[0]
idx = np.arange(0, estimate_b.shape[0])
plt.plot(data_data[idx_a], np.zeros_like(idx_a), "c*")
plt.plot(data_data[idx_b], np.zeros_like(idx_b), "m.")
plt.yticks([])
plt.title("Estimate B")
plt.xlabel("Data Value")
plt.show()
Output:
We will use: Estimate B
Performance: 77.3% correct