|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| image0.png | ||
| README.md | ||
KMeans
{:.no_toc}
* TOC {:toc}The goal
Questions to David Rotermund
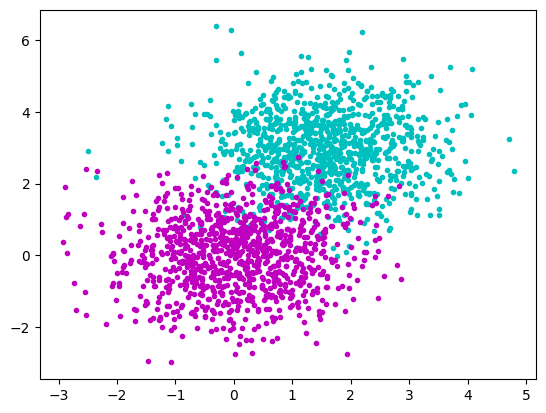
Test data
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
rng = np.random.default_rng(1)
rng = np.random.default_rng()
a_x = rng.normal(1.5, 1.0, size=(1000))
a_y = rng.normal(3.0, 1.0, size=(1000))
b_x = rng.normal(0.0, 1.0, size=(1000))
b_y = rng.normal(0.0, 1.0, size=(1000))
plt.plot(a_x, a_y, "c.")
plt.plot(b_x, b_y, "m.")
plt.show()
sklearn.cluster.KMeans and its fit
class sklearn.cluster.KMeans(n_clusters=8, *, init='k-means++', n_init='warn', max_iter=300, tol=0.0001, verbose=0, random_state=None, copy_x=True, algorithm='lloyd')
K-Means clustering.
Attribute:
cluster_centers_ : ndarray of shape (n_clusters, n_features) Coordinates of cluster centers. If the algorithm stops before fully converging (see tol and max_iter), these will not be consistent with labels_.
Method:
fit(X, y=None, sample_weight=None)
Compute k-means clustering X: {array-like, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features) Training instances to cluster. It must be noted that the data will be converted to C ordering, which will cause a memory copy if the given data is not C-contiguous. If a sparse matrix is passed, a copy will be made if it’s not in CSR format.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
rng = np.random.default_rng(1)
a_x = rng.normal(1.5, 1.0, size=(1000))[:, np.newaxis]
a_y = rng.normal(3.0, 1.0, size=(1000))[:, np.newaxis]
data_a = np.concatenate((a_x, a_y), axis=1)
b_x = rng.normal(0.0, 1.0, size=(1000))[:, np.newaxis]
b_y = rng.normal(0.0, 1.0, size=(1000))[:, np.newaxis]
data_b = np.concatenate((b_x, b_y), axis=1)
data = np.concatenate((data_a, data_b), axis=0)
kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=2, n_init = 10)
kmeans.fit(data)
plt.plot(a_x, a_y, "c.")
plt.plot(b_x, b_y, "m.")
plt.plot(
kmeans.cluster_centers_[0, 0], kmeans.cluster_centers_[0, 1], "k*", markersize=12
)
plt.plot(
kmeans.cluster_centers_[1, 0], kmeans.cluster_centers_[1, 1], "k*", markersize=12
)
plt.show()
labels_ : ndarray of shape (n_samples,) Labels of each point
What does the algorithm „think“ where the data points belong?
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
rng = np.random.default_rng(1)
a_x = rng.normal(1.5, 1.0, size=(1000))[:, np.newaxis]
a_y = rng.normal(3.0, 1.0, size=(1000))[:, np.newaxis]
data_a = np.concatenate((a_x, a_y), axis=1)
b_x = rng.normal(0.0, 1.0, size=(1000))[:, np.newaxis]
b_y = rng.normal(0.0, 1.0, size=(1000))[:, np.newaxis]
data_b = np.concatenate((b_x, b_y), axis=1)
data = np.concatenate((data_a, data_b), axis=0)
kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=2, n_init = 10)
kmeans.fit(data)
labels = kmeans.labels_
idx_0 = np.where(labels == 0)[0]
idx_1 = np.where(labels == 1)[0]
plt.plot(data[idx_0, 0], data[idx_0, 1], "r.")
plt.plot(data[idx_1, 0], data[idx_1, 1], "b.")
plt.plot(
kmeans.cluster_centers_[0, 0], kmeans.cluster_centers_[0, 1], "k*", markersize=12
)
plt.plot(
kmeans.cluster_centers_[1, 0], kmeans.cluster_centers_[1, 1], "k*", markersize=12
)
plt.show()
predict
predict(X, sample_weight='deprecated')
Predict the closest cluster each sample in X belongs to.
In the vector quantization literature, cluster_centers_ is called the code book and each value returned by predict is the index of the closest code in the code book.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
rng = np.random.default_rng(1)
a_x = rng.normal(1.5, 1.0, size=(1000))[:, np.newaxis]
a_y = rng.normal(3.0, 1.0, size=(1000))[:, np.newaxis]
data_a = np.concatenate((a_x, a_y), axis=1)
b_x = rng.normal(0.0, 1.0, size=(1000))[:, np.newaxis]
b_y = rng.normal(0.0, 1.0, size=(1000))[:, np.newaxis]
data_b = np.concatenate((b_x, b_y), axis=1)
data = np.concatenate((data_a, data_b), axis=0)
kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=2, n_init=10)
kmeans.fit(data)
x = np.linspace(data[:, 0].min(), data[:, 0].max(), 100)
y = np.linspace(data[:, 1].min(), data[:, 1].max(), 100)
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(x, y)
xx_r = xx.ravel()[:, np.newaxis]
yy_r = yy.ravel()[:, np.newaxis]
print(xx.shape) # -> (100, 100)
print(xx_r.shape) # -> (10000, 1)
print(yy.shape) # -> (100, 100)
print(yy_r.shape) # -> (10000, 1)
coordinates = np.concatenate((xx_r, yy_r), axis=1)
print(coordinates.shape) # -> (10000, 2)
labels = kmeans.predict(coordinates)
idx_0 = np.where(labels == 0)[0]
idx_1 = np.where(labels == 1)[0]
plt.plot(coordinates[idx_0, 0], coordinates[idx_0, 1], "r.")
plt.plot(coordinates[idx_1, 0], coordinates[idx_1, 1], "b.")
plt.plot(
kmeans.cluster_centers_[0, 0], kmeans.cluster_centers_[0, 1], "k*", markersize=12
)
plt.plot(
kmeans.cluster_centers_[1, 0], kmeans.cluster_centers_[1, 1], "k*", markersize=12
)
plt.show()