4.8 KiB
Code excerpt from David Rotermund, Mahbod Nouri, Alberto Garcia-Ortiz and Kaus R. Pawelzik trying to understand deep NNMF networks.
Origin of the algorithm
Refinement of the approach for deep NNMF networks shown in:
Competitive performance and superior noise robustness of a non-negative deep convolutional spiking network
David Rotermund, Alberto Garcia-Ortiz, Kaus R. Pawelzik
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2023.04.22.537923v1
Now a normal ADAM optimiser will work.
The BP learning rule is taken from here (it was derived for a spike-based SbS system, but it works exactly the same for NNMF):
Back-Propagation Learning in Deep Spike-By-Spike Networks
David Rotermund and Klaus R. Pawelzik
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/computational-neuroscience/articles/10.3389/fncom.2019.00055/full
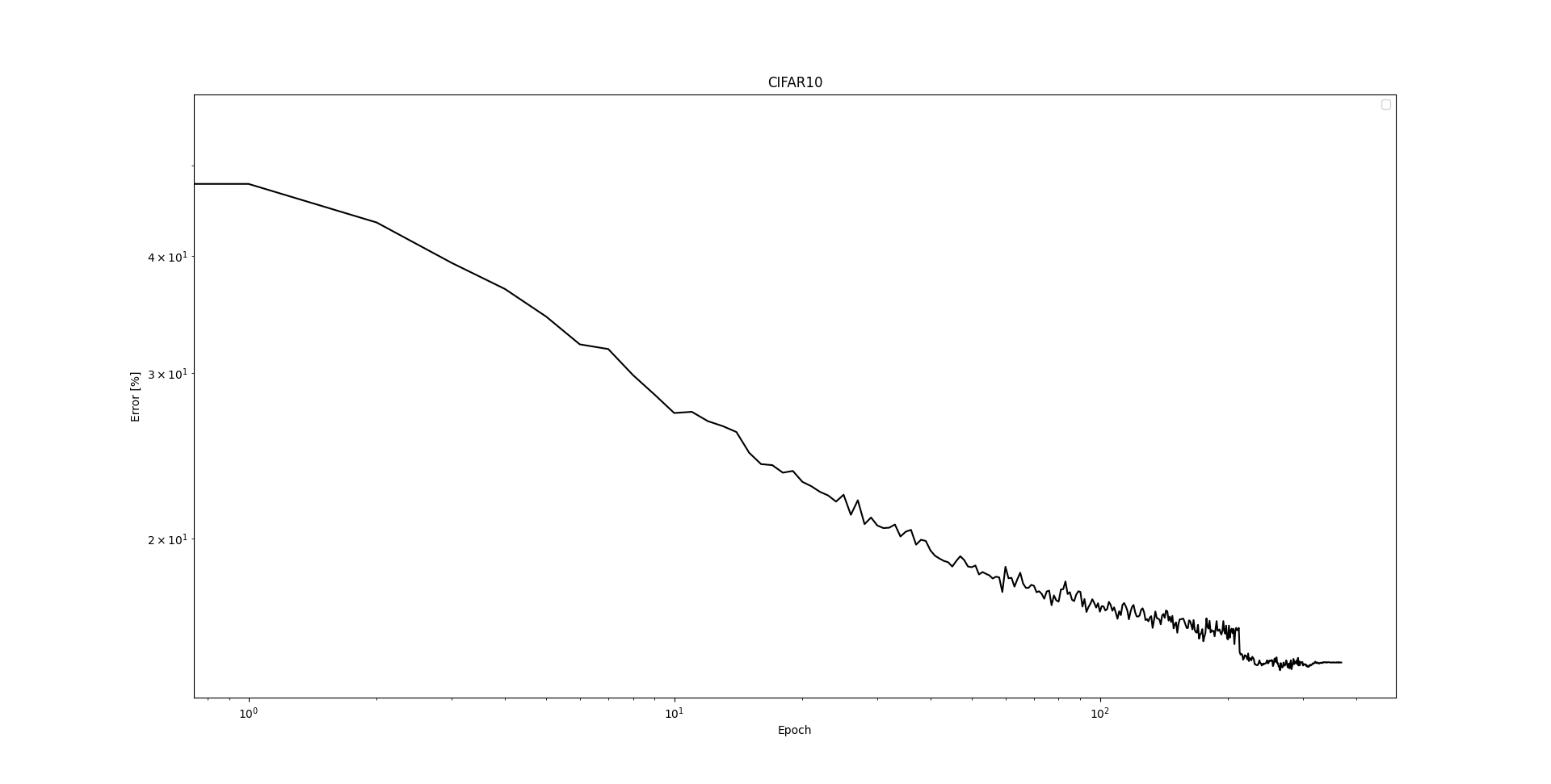
CIFAR 10 Test run on RTX 4090
Last epoch
Epoch: 369
Actual lr: 1.0000e-10 1.0000e-09 1.0000e-10
Training: Loss=0.01888 Correct=92.36%
Testing: Correct=85.25%
Time: Training=12.0sec, Testing=2.3sec
Note: This is just one run. Even though we have set the seed to a fixed value, the whole network suffers strongly under non-determinism during lerning.
Test performance
Network structure
Note: A block like
(1): Unfold(kernel_size=(5, 5), dilation=(1, 1), padding=(0, 0), stride=(1, 1))
(2): Fold(output_size=torch.Size([24, 24]), kernel_size=(1, 1), dilation=1, padding=0, stride=1)
(3): L1NormLayer()
(4): NNMF2d(75, 32, pfunctype=0, local_learning=False)
represents one(!) Conv2d NNMF Layer. We just see more of the innards that for a normal Conv2d.
Sequential(
(0): ReLU()
(1): Unfold(kernel_size=(5, 5), dilation=(1, 1), padding=(0, 0), stride=(1, 1))
(2): Fold(output_size=torch.Size([24, 24]), kernel_size=(1, 1), dilation=1, padding=0, stride=1)
(3): L1NormLayer()
(4): NNMF2d(75, 32, pfunctype=0, local_learning=False)
(5): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=False)
(6): Conv2d(32, 32, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(7): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=False)
(8): ReLU()
(9): Unfold(kernel_size=(2, 2), dilation=(1, 1), padding=(0, 0), stride=(2, 2))
(10): Fold(output_size=torch.Size([12, 12]), kernel_size=(1, 1), dilation=1, padding=0, stride=1)
(11): L1NormLayer()
(12): NNMF2d(128, 32, pfunctype=0, local_learning=False)
(13): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=False)
(14): ReLU()
(15): Unfold(kernel_size=(5, 5), dilation=(1, 1), padding=(0, 0), stride=(1, 1))
(16): Fold(output_size=torch.Size([8, 8]), kernel_size=(1, 1), dilation=1, padding=0, stride=1)
(17): L1NormLayer()
(18): NNMF2d(800, 64, pfunctype=0, local_learning=False)
(19): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=False)
(20): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(21): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=False)
(22): ReLU()
(23): Unfold(kernel_size=(2, 2), dilation=(1, 1), padding=(0, 0), stride=(2, 2))
(24): Fold(output_size=torch.Size([4, 4]), kernel_size=(1, 1), dilation=1, padding=0, stride=1)
(25): L1NormLayer()
(26): NNMF2d(256, 64, pfunctype=0, local_learning=False)
(27): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=False)
(28): ReLU()
(29): Unfold(kernel_size=(4, 4), dilation=(1, 1), padding=(0, 0), stride=(1, 1))
(30): Fold(output_size=torch.Size([1, 1]), kernel_size=(1, 1), dilation=1, padding=0, stride=1)
(31): L1NormLayer()
(32): NNMF2d(1024, 96, pfunctype=0, local_learning=False)
(33): Conv2d(96, 96, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(34): ReLU()
(35): Unfold(kernel_size=(1, 1), dilation=(1, 1), padding=(0, 0), stride=(1, 1))
(36): Fold(output_size=torch.Size([1, 1]), kernel_size=(1, 1), dilation=1, padding=0, stride=1)
(37): L1NormLayer()
(38): NNMF2d(96, 10, pfunctype=0, local_learning=False)
(39): Conv2d(10, 10, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(40): Softmax(dim=1)
(41): Flatten(start_dim=1, end_dim=-1)
)
Information about used parameters:
cnn_top: 14638
nnmf: 173344
batchnorm2d: 576
total number of parameter: 188558
We acknowledge support by the following grants: DFG: Efficient implementation of spike-by-spike neural networks using stochastic and approximate techniques (PA 569/6-1, GA 763/15-1), DFG SPP: Evolutionary optimisation of neural systems (SPP 2205) https://gepris.dfg.de/gepris/projekt/402741184 – Evolution of flexibility - optimisation of task-dependent information processing in the visual system (ER 324/5-1), Era-Net Neuron https://www.neuron-eranet.eu: I-See – Improved intra-cortical visual prostheses through complex coding and integration of spontaneous activity states (BMBF 01EW2104A), Stiftung Bremer Wertpapierboerse https://www.stiftung-bwb.de.